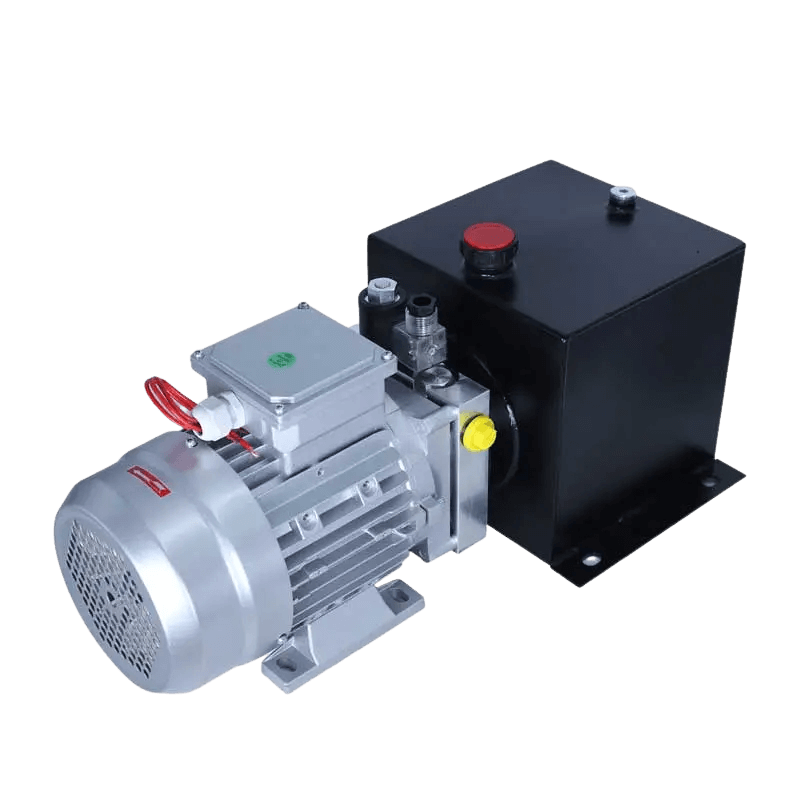
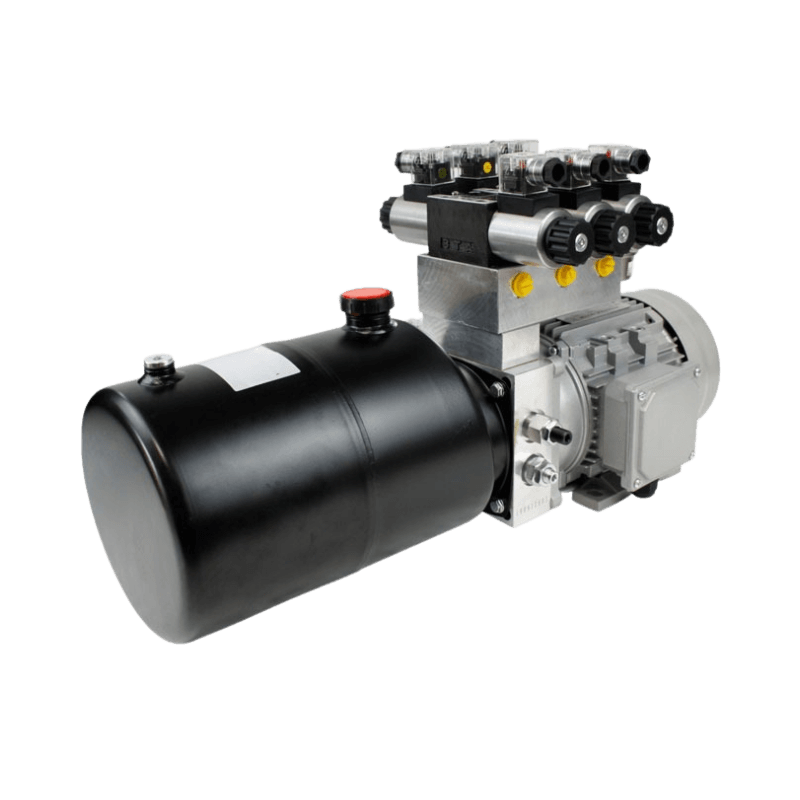
As a business owner, you may come across different types of pumps while researching industrial equipment. Two common types are pneumatic and hydraulic pumps. But what’s the difference between them?
In this article, we’ll explore these two types of pumps in greater detail, covering topics from their applications to their advantages. By the end of this article, you should have a better understanding of the key differences between them.
So if you’re ready to know more, let’s get started!
Table of contents
1. What Is Pneumatic Pump?
Pneumatic pumps, also known as air hydro pumps, are a type of pump that uses compressed air to create a vacuum. This vacuum is then used to suck up water or other fluids. They are relatively simple devices and do not require much maintenance.
Pneumatic pumps can be either positive displacement or negative displacement. Positive displacement pumps work by trapping a certain amount of fluid in a chamber and then pressurizing the chamber to force the fluid out. Negative displacement pumps work by using the vacuum created by the compressed air to suck fluid into the pump.

2. Pneumatic Pump Applications
Air-powered pumps have a wide range of applications in the industrial sector. Here are some examples of how pneumatic driven hydraulic pumps are used:

To Move Viscous Fluids
Pneumatic pumps can handle fluids with high viscosity, making them ideal for use in industries such as food processing and cosmetics manufacturing.
To Transfer Dangerous Liquids
Liquids that are flammable, toxic, or corrosive can be safely transferred using air-powered pumps. This eliminates the need for workers to come into direct contact with the liquids.
To Provide Vacuum Power
Many industrial processes require a vacuum environment. This means that the air pressure inside the chamber must be lower than the atmospheric pressure outside. Pneumatic pumps can create this vacuum by sucking the air out of the chamber.
To Power Hydraulic Systems
Hydraulic systems are commonly used in heavy machineries such as construction equipment and factory assembly lines. Pneumatic pumps are often used to provide power for these systems.
To Inflate Tires and Other Objects
Air-powered pumps can be used to quickly inflate tires, balls, and other objects. This is useful for tasks such as changing a tire on a car or inflating a basketball for a game. They can also improve worker safety by eliminating the need for manual inflation.
To Clean Surfaces
High-pressure air from a pneumatic hydraulic pressure pump can be used to clean surfaces such as floors, walls, and equipment. This is an effective way to remove dirt, dust, and other debris without the use of chemicals or water.
3. Advantages of Pneumatic Pump
Pneumatic pumps have a number of advantages over other types of pumps, including:

Energy-Efficient
Pneumatic pumps are more energy-efficient than hydraulic pumps, making them more cost-effective to operate. They are also less likely to overheat, which can possibly damage equipment.
Quiet Operation
Pneumatic pumps typically operate more quietly than hydraulic pumps, making them ideal for use in noise-sensitive environments. If you’re using it in an agricultural or industrial setting, the lack of noise can be a major advantage.
Low Maintenance
Pneumatic pumps require less maintenance than hydraulic pumps, making them more convenient to operate. Additionally, they are less likely to break down, which can save you money in the long run.
High-Pressure
Pneumatic pumps are capable of operating at higher pressures than other types of pumps, making them ideal for use in demanding applications.
4. What Is a Hydraulic Pump?
A hydraulic pump is a mechanical device that converts mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. This conversion of energy is used to create pressure or force, which can then be used to power hydraulic cylinders or motors. Hydraulic pumps are used in a wide variety of applications and they are typically powered by either an electric motor or a gasoline engine.
These pumps consist of several different parts, each of which plays an important role in the overall function of the unit.
- Reservoir – It is where the hydraulic fluid is stored, and it also helps to cool the fluid as it circulates through the pump.
- Piston – It is responsible for moving the fluid through the pump, and it is connected to the crankshaft via a connecting rod.
- Pump – It is the main component of the hydraulic pump, and it is responsible for moving the fluid through the system.
- Valves – They control the flow of fluid through the pump, and they are opened and closed by the crankshaft.
- Seals – They help to prevent leakage and keep the hydraulic fluid from escaping into other parts of the engine.
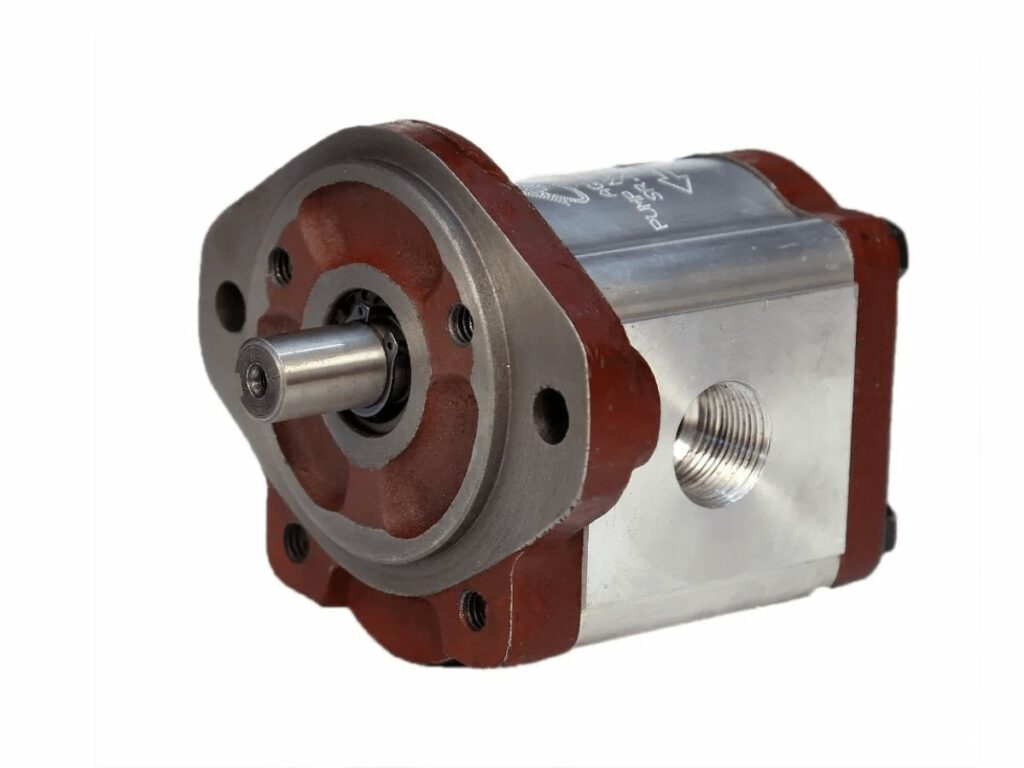

5. Hydraulic Pump Application
Hydraulic pumps are widely used in industrial applications where a power source is needed to generate a high force or create movement. Here are the common hydraulic pump industrial applications:
Construction Equipment
Hydraulic pumps are used in construction equipment such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes. They provide the power needed to operate the machine’s hydraulic cylinders, which are used to move the various parts of the machine.
Industrial Machinery
Hydraulic pumps are used in many types of industrial machinery, such as presses, die-cast machines, and plastic injection molding machines. They provide the power needed to operate the machine’s hydraulic cylinders, which are used to move the various parts of the machine.
Automotive Manufacturing
Hydraulic pumps are used in automotive manufacturing to testing car components for strength and durability. The hydraulic cylinders apply pressure to the component being tested, simulating the forces that it will experience during use.
Food Processing
Hydraulic pumps are used in food processing applications such as canning and packaging. They provide the power needed to operate the machine’s hydraulic cylinders, which are used to move food products through the process.
Oil and Gas Production
Hydraulic pumps are used in oil and gas production applications such as drilling and fracking. They provide the power needed to operate the machine’s hydraulic cylinders, which are used to move heavy equipment and materials around the job site.
Water treatment
Hydraulic pumps are also used in water treatment applications such as filtration and purification. They provide the power needed to operate the machine’s hydraulic cylinders, which are used to move water through the treatment process.
6. Advantages of Hydraulic Pump
Hydraulic pumps offer a wide range of benefits that make them ideal for a variety of applications. Here are some of the main advantages of hydraulic pumps:

Powerful Tool
Hydraulic pumps are very powerful tools. They can generate a lot of force, which makes them ideal for applications where large amounts of force are required.
Precision
These pumps are also very precise. They can generate a lot of force while still maintaining a high degree of control. This is essential for applications where precise movements are required.
Versatile
Hydraulic pumps are also very versatile. They can be used for a wide variety of applications and they offer a wide range of pressure and flow rates which makes them a great choice for many different industries.
Safe to Use
These pumps not only display a higher level of safety performance but are also equipped with multiple security features making them even safer for the user.
Operates in Harsh Conditions
Hydraulic pumps can be used in a variety of harsh conditions. They are designed to withstand high temperatures and pressures, making them ideal for use in industrial environments.
7. The Key Difference Between Hydraulic and Pneumatic Pumps
While hydraulic and pneumatic pumps have a lot in common, there are key differences that set them apart. Let’s take a look at these key differences in detail.
| Hydraulic Pumps | Pneumatic Pumps |
|---|---|
| uses fluid to create pressure | uses air to create pressure |
| need to contain a lot of fluid | only need to contain a small amount of air |
| can create more pressure | use air, which is compressible and limits the amount of force generated by the pump |
| typically used in heavy-duty applications where a lot of force is needed | usually used in lighter applications where less force is required |
| more likely to break down and require more maintenance | less expensive and easier to maintain |
Operation
This is the most notable difference between the two types of pumps. A hydraulic pump uses fluid to create pressure, while a pneumatic pump uses air to create pressure.
Size
Another key difference between hydraulic and pneumatic pumps is their size. Hydraulic pumps are typically much larger than pneumatic pumps because hydraulic pumps need to contain a lot of fluid, while pneumatic pumps only need to contain a small amount of air.
Pressure
The pressure that each type of pump can create is also different. 10000 PSI air hydraulic pumps can create more pressure than pneumatic pumps because hydraulic fluids are much denser than air, meaning they can take more pressure. Pneumatic pumps use air, which is compressible and limits the amount of force generated by the pump.
Applications
Hydraulic pumps are typically used in heavy-duty applications where a lot of force is needed. They are commonly found in construction equipment, manufacturing machinery, and other industrial settings.
Pneumatic pumps, on the other hand, are usually used in lighter applications where less force is required. They are commonly found in air tools, pneumatic cylinders, and other similar devices.
Complexity
Hydraulic pumps are typically more complex than pneumatic pumps because they have more moving parts. This also means that they are more likely to break down and require more maintenance.
Cost
Lastly, hydraulic pumps are generally more expensive than pneumatic pumps because they require specialized components and skills to maintain them. Pneumatic pumps are less expensive and easier to maintain, making them a more popular choice for many applications.
If you want to learn more about the differences between hydraulic and pneumatic system, check this video!
8. 7 Factors To Consider When Choosing Between Hydraulics and Pneumatics
Hydraulic and pneumatic systems are both used in a variety of industrial applications. When choosing between the two, here are the 7 factors you need to consider:
#1 Power Source
Hydraulic systems use a liquid as the power source, while pneumatic systems use gas. If you need a system that can run on a variety of power sources, then air hydraulic pumps may be the better option. Air driven hydraulic pumps can run on water, oil, or even air pressure.
Pneumatic systems, on the other hand, require a constant supply of gas, such as compressed air. This can be a problem if there is a power outage or if the gas supply is interrupted.
#2 Ease of Installation
Hydraulic systems are generally more complex than pneumatic systems and require a trained technician for installation. Pneumatic systems are relatively simple and can be installed by someone with basic mechanical knowledge. They are also typically smaller than hydraulics, which makes them easier to install in limited spaces.
#3 Application
If you’re looking to buy a system for a specific application, it’s important to research whether hydraulics or pneumatics is better suited.
As a general rule, hydraulics are better for heavy-duty applications that require a lot of power, such as lifting or moving heavy objects. Pneumatics are typically used in lighter applications where precise control is more important than raw power, such as in assembly line tasks.
#4 Pressure Rating
The pressure rating is the maximum amount of pressure that the system can withstand. Hydraulic systems have higher pressure ratings than pneumatic systems and can typically withstand pressures up to 10,000 PSI. Pneumatic systems have lower pressure ratings, usually around 100 to 200 PSI.
#5 Flow Rate
The flow rate is the amount of liquid or gas that can be moved through the system per unit of time. Hydraulic systems have higher flow rates than pneumatic systems since liquids are easier to move than gases.
#6 Maintenance Requirements
Both hydraulic and pneumatic systems require regular maintenance to keep them running smoothly. However, hydraulic systems are usually more complex and require more frequent maintenance than pneumatic systems.
Pneumatic systems have fewer moving parts than hydraulics and typically don’t require as much upkeep. However, they do require a clean, dry air supply to prevent corrosion and malfunction.
#7 Cost
Finally, you’ll need to consider the cost of the system when choosing between hydraulics and pneumatics. Hydraulic systems are typically more expensive than pneumatic systems since they are more complex.
Pneumatic systems are less expensive to purchase and maintain, but they may not have the same power or precision as hydraulic systems.
9. Conclusion
Now that you know how the pneumatic and hydraulic pump differs, you can make a more informed decision about which type of pump is best for your needs. If you’re looking to buy these tools for your business, it’s better to work with a reputable manufacturer who can offer you a top-quality product and provide reliable customer service.
Here at Uphyd, we understand that you need a reliable and powerful hydraulic power pack to get the job done right. Contact us today to help you select the perfect power pack for your business needs!